If you’re serious about tracking and optimizing traffic campaigns, there’s one tool you need to master: Google Tag Manager (GTM).
It’s one of the most powerful — and underrated — tools in a traffic manager’s toolkit. With GTM, you can manage tracking codes, measure conversions, and pass important data to Google Ads, Meta Ads, and Google Analytics 4, all without constantly bothering a developer.
In this article, you’ll learn what GTM is, why it’s essential for traffic campaigns, and how to start using it to level up your results.
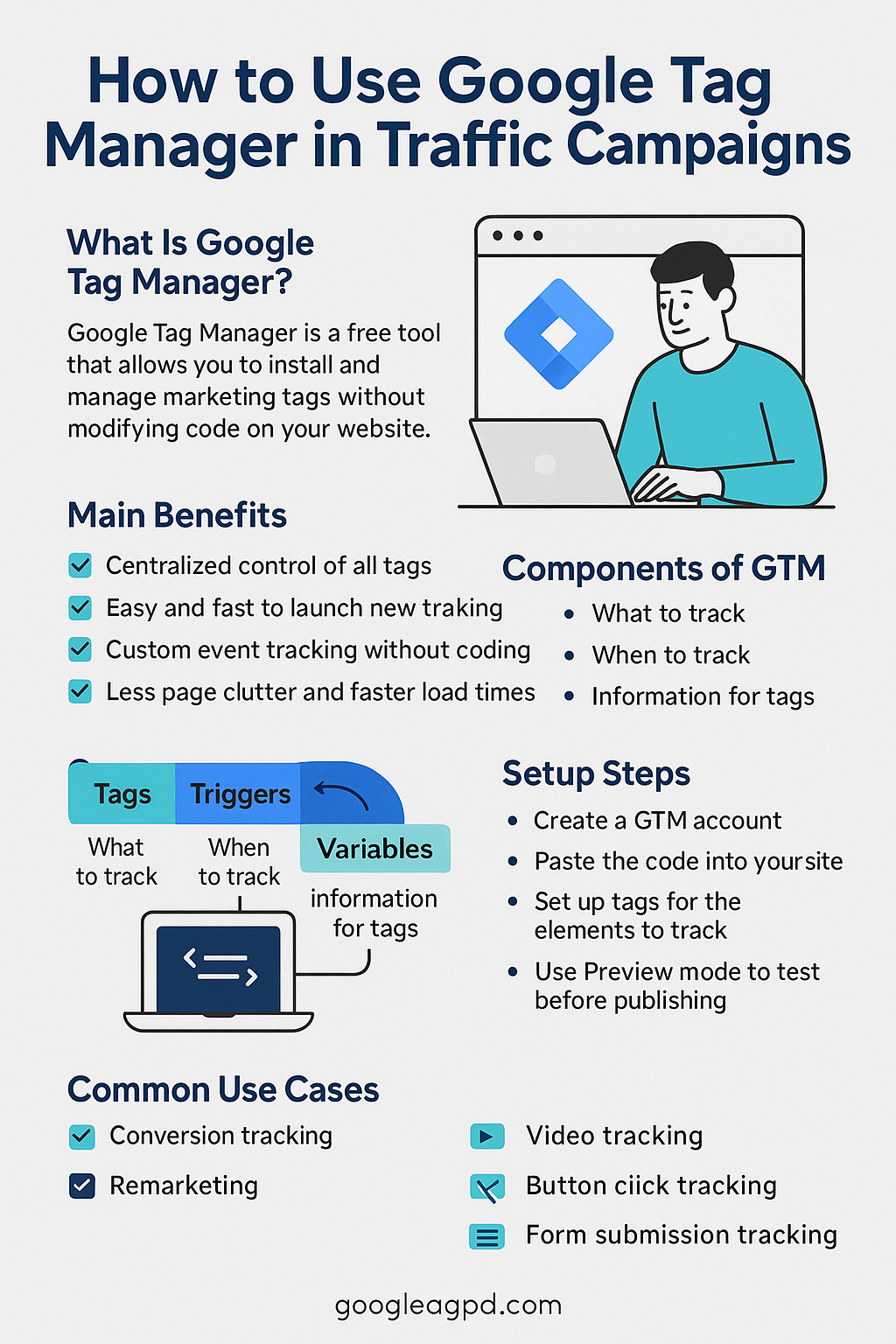
What Is Google Tag Manager?
Google Tag Manager is a free tool from Google that allows you to manage marketing tags and tracking pixels on your website — without editing the site’s code manually every time.
With GTM, you can install:
- Google Ads conversion tracking
- Meta (Facebook) Pixel
- Google Analytics (GA4)
- Custom event tracking
- Scroll depth, clicks, form submissions, and more
All from one clean dashboard.
Why Traffic Managers Should Use GTM
✅ 1. Centralized Control
No need to add scripts directly to the website — manage everything in one place.
✅ 2. Fast Implementation
Launch tracking in minutes instead of waiting days for developer help.
✅ 3. Custom Event Tracking
Track specific actions like:
- Button clicks
- Form submissions
- Page scrolls
- Video plays
- Add to cart behavior
✅ 4. Cleaner Code
Instead of loading 10+ scripts on your site, GTM keeps your tracking organized and optimized.
How GTM Works: The Basics
GTM works through 3 core components:
1. Tags
These are the scripts or codes you want to fire — like Google Ads conversion tags, GA4, or Meta Pixel.
2. Triggers
These define when a tag should fire — e.g., on a page view, form submission, or button click.
3. Variables
These are pieces of information passed to your tags — like page URLs, click text, or event values.
Together, they allow you to track anything, without touching code.
How to Set Up Google Tag Manager (Step-by-Step)
Step 1: Create a GTM Account
- Go to tagmanager.google.com
- Click “Create Account”
- Add your website and select Web Container
Step 2: Install GTM on Your Website
After creating the container, GTM gives you two code snippets to place on every page of your site.
💡 You only do this once — then you can add all future tags from GTM itself.
Use:
- WordPress GTM plugin
- Direct placement in your theme’s header
- Developer assistance for other platforms
Step 3: Add Your First Tags
Example: Add Google Analytics 4
- Click “Add a New Tag”
- Choose “Google Analytics: GA4 Configuration”
- Enter your GA4 Measurement ID
- Set trigger to “All Pages”
- Name the tag and publish
✅ Done — you’ve added GA4 via GTM.
Example: Add Google Ads Conversion Tag
- In Google Ads, go to Tools > Conversions
- Create a new conversion action (e.g., form submission)
- Choose “Use Google Tag Manager”
- Copy the Conversion ID and Label
- In GTM, create a new tag > “Google Ads Conversion Tracking”
- Paste the ID and Label
- Choose the correct trigger (e.g., Thank You Page view or button click)
Example: Add Meta Pixel
- In Meta Events Manager, choose your Pixel
- Select “Add via Partner Integration” > “Google Tag Manager”
- Follow the steps or manually add the Pixel code via a Custom HTML tag in GTM
- Set it to fire on All Pages
Then you can add Standard Events or Custom Events for actions like “Lead” or “Purchase.”
Tracking Button Clicks and Form Submissions
Want to track conversions when someone clicks a button?
- Enable click variables in GTM:
- Go to Variables > Configure > Check “Click Classes,” “Click ID,” etc.
- Create a Trigger:
- Trigger Type: “Click – All Elements”
- Conditions: e.g., Click ID contains “submit-button”
- Create a Tag:
- Choose Google Ads, Meta, or GA4 event
- Attach it to your new trigger
- Publish
Now you can track specific user actions beyond just page views.
Testing Tags with Preview Mode
Always use GTM’s Preview Mode before publishing:
- Click Preview in GTM
- Enter your website URL
- Interact with the site
- See which tags fired and troubleshoot any issues
For deeper insights, install the Tag Assistant Chrome Extension.
Common GTM Use Cases for Traffic Managers
- Track lead form submissions (even on multi-step funnels)
- Fire different conversion events per campaign
- Create custom conversion goals in GA4
- Trigger scroll depth events to build remarketing audiences
- Control tags based on country, page, or user behavior
GTM Best Practices
- Name your tags, triggers, and variables clearly
- Keep a spreadsheet log of all installed tags
- Test regularly — especially after site updates
- Use folders to organize campaigns by client or platform
- Avoid duplicate tags (don’t install GA4 both via GTM and hardcoded)
Final Thoughts: GTM = More Control, More Precision
Mastering Google Tag Manager puts you in control of your tracking — and that gives you the power to measure, improve, and scale your traffic campaigns with confidence.
It may seem technical at first, but once you get used to it, you’ll wonder how you ever ran paid ads without it.
Less guesswork. More data. Better results.